Image Recognition Based Location for Indoor Positioning. Application at the Valentino Castle (Torino)
Keywords:
Indoor Positioning, LiDAR, RGB-D images, Image Recognition Based Location, databaseAbstract
This paper describes the result of the application of an Image Recognition Based Location (IRBL) method, focused on the creation of a database of solid images (RGB-D) for a mobile application. The activity described was carried out to test the positioning method developed within a research project conducted by the Politecnico di Torino (directed by Prof. Andrea Lingua) in collaboration with the South Korean research institute ETRI (Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute), with the aim of creating an indoor positioning procedure based on image recognition, for purposes related to security in public places.
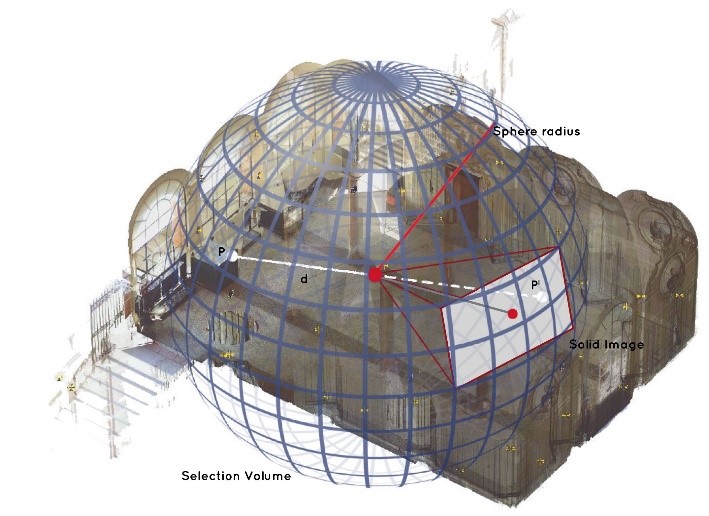
In a preliminary stage, a LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) survey of the environment was carried out, obtaining a complete three-dimensional model needed to estimate the position of the camera and the orientation parameters. From this model, a database of synthetic reference images was generated, creating a set of images in different directions and with different angles for each scan centers. After the data acquisition phase, the information relating to the distances and the external orientation parameters (X, Y, Z, ω, φ and κ) extracted from the images in the database, were used in the positioning procedure, as a reference for the estimation of the camera position of the images acquired with the mobile device. The following paper will describe the survey operations, the method used to generate the database of solid images with the subsequent positioning procedure and, finally, the results obtained following the validation of the test.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



